Tujuh Alat Manajemén jeung Rarancang
Tujuh Alat Manajemén jeung Rarancang (basa Inggris: Seven Management and Planning Tools) asal muasalna aya dina gawe Panalungtikan Operasi sanggeusna Perang Dunya II jeung panalungtikan Total Quality Control (TQC) urang Jepang. Dina taun 1979, buku Seven New Quality Tools for Managers and Staff diterbitkeun sarta taun 1983 dialihbasakeun kana basa Inggris.
Tujuh alat éta nyaéta:
- Affinity Diagram (KJ Method)
- Interrelationship Diagraph (ID)
- Tree Diagram
- Prioritization Matrix
- Matrix Diagram
- Process Decision Program Chart (PDPC)
- Activity Network Diagram
|
|
Artikel ieu keur dikeureuyeuh, ditarjamahkeun tina basa Inggris. Bantuanna didagoan pikeun narjamahkeun. |
Tujuh alat
[édit | édit sumber]Affinity Diagram
[édit | édit sumber]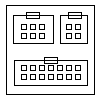
This tool takes large amounts of disorganized data and information and enables one to organize it into groupings based on natural relationships. It was créated in the 1960s by Japanese anthropologist Jiro Kawakita.
Interrelationship Diagraph
[édit | édit sumber]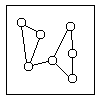
This tool displays all the interrelated cause-and-effect relationships and factors involved in a complex problem and describes desired outcomes. The process of créating an interrelationship diagraph helps a group analyze the natural links between different aspects of a complex situation.
Tree Diagram
[édit | édit sumber]
This tool is used to bréak down broad categories into finer and finer levels of detail. It can map levels of details of tasks that are required to accomplish a goal or task. It can be used to bréak down broad general subjects into finer and finer levels of detail. Developing the tree diagram helps one move their thinking from generalities to specifics.
Prioritization Matrix
[édit | édit sumber]
This tool is used to prioritize items and describe them in terms of weighted criteria. It uses a combination of tree and matrix diagramming techniques to do a pair-wise evaluation of items and to narrow down options to the most desired or most effective.
Matrix Diagram
[édit | édit sumber]
This tool shows the relationship between items. At éach intersection a relationship is either absent or present. It then gives information about the relationship, such as its strength, the roles played by various individuals or méasurements. Six differently shaped matrices are possible: L, T, Y, X, C, R and roof-shaped, depending on how many groups must be compared.
Process Decision Program Chart (PDPC)
[édit | édit sumber]
A useful way of planning is to bréak down tasks into a hierarchy, using a Tree Diagram. The PDPC extends the tree diagram a couple of levels to identify risks and counterméasures for the bottom level tasks. Different shaped boxes are used to highlight risks and identify possible counterméasures (often shown as 'clouds' to indicate their uncertain nature). The PDPC is similar to the Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMéa) in that both identify risks, consequences of failure, and contingency actions; the FMéa also rates relative risk levels for éach potential failure point.
Activity Network Diagram
[édit | édit sumber]
This tool is used to plan the appropriate sequence or schedule for a set of tasks and related subtasks. It is used when subtasks must occur in parallel. The diagram enables one to determine the critical path (longest sequence of tasks). (See also PERT diagram.)
Rujukan
[édit | édit sumber]Bacaan salajengna
[édit | édit sumber]- Brassard, M. (1996) The Memory Jogger Plus+. ISBN 1-879364-83-2.
- Seven New Management and Planning Tools
Tumbu kaluar
[édit | édit sumber]- American Society for Quality - official Web site
- The 'New' Tools Archived 2007-02-16 di Wayback Machine from Vanderbilt University
